はじめに
docker をbuild中にErrorがでてbuildできなくなった。
One of the configured repositories failed (Unknown),
and yum doesn't have enough cached data to continue. At this point the only
safe thing yum can do is fail. There are a few ways to work "fix" this:
1. Contact the upstream for the repository and get them to fix the problem.
2. Reconfigure the baseurl/etc. for the repository, to point to a working
upstream. This is most often useful if you are using a newer
distribution release than is supported by the repository (and the
packages for the previous distribution release still work).
3. Disable the repository, so yum won't use it by default. Yum will then
just ignore the repository until you permanently enable it again or use
--enablerepo for temporary usage:
yum-config-manager --disable <repoid>
4. Configure the failing repository to be skipped, if it is unavailable.
Note that yum will try to contact the repo. when it runs most commands,
so will have to try and fail each time (and thus. yum will be be much
slower). If it is a very temporary problem though, this is often a nice
compromise:
yum-config-manager --save --setopt=<repoid>.skip_if_unavailable=true
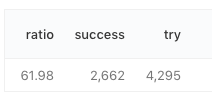
Insufficient space in download directory /var/cache/yum/x86_64/latest/amzn-main
* free 0
* needed 100 k
原因
dockerのdiskがfullになっている
対処
使っていないdocker container、docker imageを削除する
% docker rm `docker ps -aq` 38068772176a 3888aa5447b1 66fe52df5528 82584720485f 5bd5855641fd 379ca80b607c e06a7e7e1e60 5685e43f3a4a e3b182bbb54d
% docker images | awk '{print $3}' | xargs docker rmi
Deleted: sha256:aea654465ef677aeb2b9e25eb8b9fc4a8b1aa23908c229249898cf2e2b9d4ed9
Deleted: sha256:cf346c3b10cd250b10af438fbf1554781a38c243dd873b66dc2b07f82a8375ca
Deleted: sha256:16ecc35ae52fd0fbc6428510ac554549227baf58e053937d5b7f6732595d057f
Deleted: sha256:9e6d8d236b08a8f4eabdbd661d8caa80e87db8f663894334f3b19a79bdc15a0a
Deleted: sha256:c834d9fa415cddfd8c6d3ebd726816007529348e7abd6be47cbc021955b3ea5c
Deleted: sha256:7d2ad60980725a5cb256bafc8b0df8a0b4c41b6e754063164c793888c2239ff0
Deleted: sha256:518874706ae596a3f69c7f6e93c9095b7284e5c20c6c1c80c8ab8b924a1049e9
Deleted: sha256:cd217551e011d423ad768be44bab435e8bb6f7ff71276c1288ff2477541bf353